International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Developmental Research
Salvia Rosmarinus: A Comprehensive Review of its Phytochemical Composition and Pharmacological Properties
Rahal El Kahkahi1*, Meryama Moustaine2 and Rachid Zouhair1
1Laboratory of Plant Biotechnology and Molecular Biology, Faculty of Science, University Moulay Ismail, PO. Box 11201, Zitoune, Meknes 50000, Morocco
2Laboratory of Botany and Plant Protection, Faculty of Sciences, University Ibn Tofail, Kenitra, Morocco
Cite this as
Kahkahi RE, Moustaine M, Zouhair R. Salvia Rosmarinus: A Comprehensive Review of its Phytochemical Composition and Pharmacological Properties. Int J Pharm Sci Dev Res. 2025;11(1):001-005. DOI: 10.17352/ijpsdr.000055Copyright License
© 2025 Kahkahi RE, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Sacred since Antiquity for its virtues, the use of Rosemary has continued through the ages as an aromatic and medicinal plant. Today, it is an interesting alternative to environmental issues in the pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetics. Rosemary, native to the Mediterranean basin, is a branchy, bushy evergreen shrub with persistent leaves. In this review we have established a monograph on Salvia Rosmarinus, that is the botanical description, the taxonomic classification, its origin and distribution, and their benefits, and the chemical constituents of the essential oil.
Introduction
Since ancient times, man has used various resources found in his environment to treat all kinds of diseases. Currently, the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that about 80% of the world’s inhabitants use traditional herbal preparations as primary health care [1].
Morocco, through its biogeographical position, offers a very great ecological and floristic diversity estimated at more than 5350 species belonging to several botanical families, of which 18% are endemic and remain very little explored on the phytochemical and pharmacological levels [2].
Among the inventory of the most popular medicinal plants in Morocco, we cite Salvia Rosmarinus L., known as rosemary, which is the subject of recent research in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and agri-food fields. It is an aromatic shrub of the Lamiaceae family, appreciated for its antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, hepatoprotective, neuroprotective properties are widely used in the manufacture of medicines and in traditional medicine [3-5].
In Morocco, rosemary grows in association with the Aleppo pine (Pinus halepensis) and the maritime pine (Pinus mogrebiana). It occupies large areas in the West. In 2014, Morocco exported nearly 8000 tons of dry rosemary matter to the world. They are used to extract the active ingredients sought after in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food industries. Rosmarinus officinalis is a plant of great ecological and economic interest [6].
Botanical description
Rosemary is a very fragrant, bushy, xerophytic, strongly branched, evergreen shrub or woody subshrub that can reach up to 2 meters in height [7]. It is a stimulating antiseptic plant with a strong odor appreciated for its biological properties [8].Roots: This is the underground organ that is used for fixing the ground and drawing water and nutrients necessary for the plant, they are deep and pivotal [9].
- Leaves: The leaves carried by subrounded branches, are opposite and sessile, narrow, and lanceolate, 10mm to 25 mm long and 1.5 mm wide: their shape is stiff, their texture hard and leathery, their blades thick, brittle, dark green on the upper surface and whitish on the lower surface, its edges are rolled on the underside and the midrib is prominent [10].
- Stems: Shrub or subchrub, a branch of 0.5 to 2 meters this stem is tortuouns, angular and fragile. The bark is linear with a cyme of more or less stimulation ears [9,11].
- Flowers: The flowers are grouped dis small terminal axillary clusters, arranged in the axil of the leaves, the bilabiate calyx has the shape of an oval and downy bell, and the corolla is long tubular, 1.2 cm wide, pale blue, lilac, or white but often spotted with small purple spots [12].
- Fruit: The fruit is a smooth and globular tetrachene, dark brown and 2.3 mm long [13]. Flowering begins in February and sometimes January depending on the climate and continues until April-May [14].
Mode of reproduction and dissemination in nature
Reproduction can be done sexually (seed) and asexually (cutting and bursting of tufts). Its specific modes of dissemination are Gravity, wind, water, animals (mammals, birds, insects, etc.), and humans [15].
Ecology, geographical distribution
Rosemary has a very large geographical area, it grows on all types of terrain with a preference for calcareous, clayey, clayey-silty soils located in sunny, hot, dry, and wind-sheltered places. It is widespread on most scrublands, garrigues, on seashores, it is found up to 1500 m altitude. It often accompanies the Aleppo pine, Sage, and Thyme [16].
Internationally, rosemary is widespread in Africa: Morocco, Tunisia, and Algeria. In Europe, particularly in the Iberian Peninsula, it is widely present in Catalonia, Andalusia, Southern Portugal, and France. It also reappears in Turkey and Greece and is abundant on the Dalmatian coast, especially in Italy [14].
In Morocco, rosemary is located on the banks of the Moulouya, the Rif Atlas, the Middle Atlas, the Great Atlas, and the Oriental region. The Oriental region accounts for the lion’s share of 50.22% and contains the largest areas of rosemary on a national scale. It constitutes the granary of Morocco in terms of rosemary production, followed by the Fez-Meknes region and the Draa-Tafilalet region [17].
Chemical composition of rosemary
The chemical composition of the plant depends on the place of growth and harvest as well as the time of harvest in the vegetative cycle [18]. The dried leaves and essential oil (Spanish type and Morocco-Tunisia type) of Salvia Rosmarinus are listed as herbal drugs in the European Pharmacopoeia 11th edition [19].
Essential oil: represents 1 to 3% of the plant contains: apinene (7 to 80%), verbenone (1 to 37%), camphor (1 to 35%) eucalyptol (1 to 35%), borneol (4 to 19%), bornyl acetate (up to 10%) and camphene. In addition to the essential oil, rosemary contains: 2 to 4% of triterpene derivatives such as: ursolic acid, oleanolic acid, germanicol acetate, diterpene lactones: picrosalvine, derivatives of canosolic acid, romanol, romadial, phenolic acids, hydroxylated fatty acids, especially derivatives of decanoic acid, organic fatty acids: Citric, glycolic and glyceric acid, sterols, choline mucilage and resin [13,20,21].
Pharmacological activity of rosemary (Salvia Rosmarinus)
Rosemary is reported to be used in traditional and modern medicine for the treatment of various diseases and conditions as antispasmodic, renal colic, antirheumatic, diuretic, antiepileptic, expectorant, against diabetes, dysmenorrhea, heart disease, and relieve respiratory disorders, etc. (Figure 1). It has also been used for analgesic purposes against abdominal pain, stomachache, and sore throat. In addition, it has been used as a tonic to improve memory dysfunction, especially during excessive physical or mental work. In addition, the plant is known to be used as an insecticide and herbicide among many other reported uses [22-25]. In gastronomy, rosemary is widely used as a condiment in the Mediterranean basin and England to flavor meats, fish, and vegetables. There is honey specially produced from the nectar of rosemary flowers. This very fragrant honey is called rosemary honey. Its aromatic taste allows it to replace vanilla to enhance cakes [26]. In cosmetics, rosemary oils have been widely used for centuries, as an ingredient in beauty products and soaps. In addition, it accelerates hair growth, its essential oil is used in the composition of many perfumes [27].
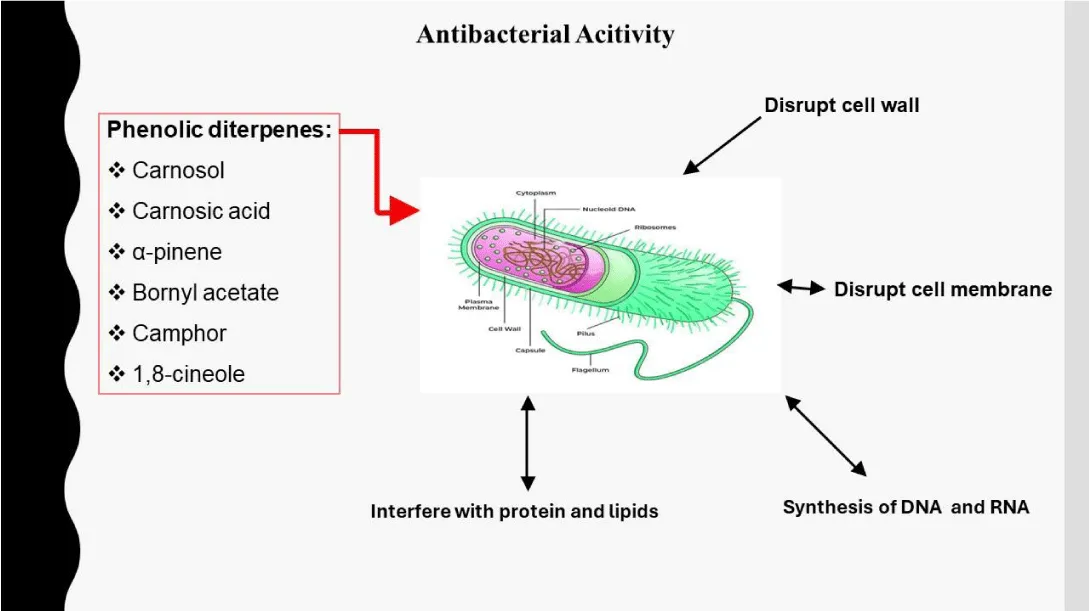
- Antimicrobial activity of rosemary: It has been reported that some compounds in rosemary extract have antimicrobial properties. The antimicrobial activities of rosemary oil and extract have been demonstrated in vitro against a broad spectrum of Gram-negative and positive bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus albus, Vibrio cholerae, Escherichia coli, Brochothrix thermosphacta, Bacillus cereus, Clostridium perfringens, Aeromonas hydrophila, and Salmonella choleraesuis. The compounds responsible for this activity are phenolic diterpenes carnosol and carnosic acid, a-pinene, bornyl acetate, camphor, and 1, 8-cineole. The mechanism by which these molecules inhibit bacteria is by affecting the functioning and composition of the cell membrane, and the synthesis of DNA, RNA, Proteins, and Lipids (Figure 2) [28]. In addition, Salvia Rosmarinus essential oil has been shown to inhibit the adhesion of Candida albicans by denaturing cellular structures and altering membrane permeability [3,28,29-32].
- Anti-fungal activity of rosemary: Aflatoxin B1 is a highly toxic and carcinogenic metabolite produced by Aspergillus species on food and agricultural commodities [33]. This biosynthesis was completely inhibited by rosemary essential oil at a concentration of 450 ppm. The results indicated the potential of this essential oil as a natural preservative against Aspergillus parasiticus [34].
- Using the standard technique of diffusion on agar, evaluated the biological activity of 11 essential oils including that of Rosemary, the results showed that these oils have a moderate inhibitory on the five yeasts (Candida albicans, Rhodotorulaglutinis, Schizoccharomycespombe, saccharomycecescerevisiae, Yarrowilypolitica) tested [35-37].
- Antiviral activity: The evaluation of the antiviral activity of the commercial extract of rosemary showed that there is an inhibition of infection by the Immunodeficiency virus (HIV) at a very low concentration. However, carnasol showed an anti-viral activity (Anti-HIV) at a moderate concentration which was not cytotoxic [38].
- Ovicidal activity: Rosemary oil was found to be an ovicidal agent against three species of mosquitoes (Anopheles stephensi, Aephensi, and Culex quinquefasciatus) [39]. Prajapati, et al.2005[40]found that this oil exhibits repellent activity against mosquitoes (Aedesaegypti).
- Antioxidant activity: The antioxidant activity of rosemary has been known for about 30 years [41]. Due to its antioxidant properties, rosemary is widely used as a spice with the highest antioxidant activity [42].
- Several authors have studied the use of rosemary extracts as an antioxidant to preserve meat products [41,43,44].
- Anti-inflammatory activity of rosemary: Rosemary has exhibited potent anti-inflammatory mechanisms; rosemary essential oil and extract were found to significantly inhibit leukocyte migration in vivo. It can reduce the number of leukocytes at the site of inflammation, leading to an anti-inflammatory response. Rosemary extract also inhibited other pro-inflammatory substances such as nitric oxide and inflammation-associated genes. The anti-inflammatory activity of rosemary most likely depends on a synergistic mechanism between several of its components [28].
- Anticancer activity: Thanks to some components (Carnosol, Rosmaridipherol, Rosmanol, and Rosmarinic acid), rosemary is considered as a cancer therapy [45,46].
- Many studies have reported on the anticancer mechanisms of rosemary, they have demonstrated significant antiproliferative activities against several human cancer cell lines. Also, the main compounds of rosemary extract have been shown to induce apoptosis in cancer cells. This activity can be used in future cancer treatments and warrant further research [3].
- Hypoglycemic effect: Observation after oral administration of different doses of the ethanolic extract of Rosemary to 3 groups of rabbits (rabbits with normal glycemia, rabbits with hyperglycemia induced by oral administration of Glucose, and alloxan diabetic rabbits have clearly shown that this extract exerts a remarkable hypoglycemic activity at a dose of 200 mg/Kg [47].
- Anti-acetyl-cholisterase effect: Aqueous and methanolic extracts of 11 plants used in traditional Chinese medicine for memory enhancement were studied to evaluate their acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activities using the Ellman colorimetric method. The methanolic extract of rosemary showed a moderate inhibition (17%) of the enzyme at a concentration of 0.1% [48].
- Anti-hepatotoxic effect: Many studies have been conducted to study the anti-hepatotoxic effect of rosemary, the work was concentrated on the evaluation of the efficacy of the methanolic extract of rosemary to normalize some histological and biochemical parameters of the Liver, after the ingestion of a hepato-toxin carbon tetrachloride (CCL4). The results indicated that this extract prevented lipid peroxidation (information, necrosis, normalized bilirubin levels, glycogen, and alanine aminotransferase activity) and finally it increased glutathione-S-transferase (GST) activity [49,50].
- Food preservation: Rosemary is a good and natural source of antioxidant compounds. It is widely used in the food industry to prevent possible oxidative and microbial degradation of foods [51].in cooking, it is advisable to use a few leaves when cooking (Meats, chicken, vegetables, fish, and shellfish), because its bactericidal properties help reduce toxins and putrefaction [52].
- Cosmetics: Rosemary is used in the composition of perfumes, especially masculine, aromatic woody citrus, and aromatic ferns, as well as in the formulation of skin ointments [51] For their aromatic power and their regenerating and moisturizing action [52-56].
Conclusion
Rosemary has shown interesting potential as a natural food preservative and as a therapeutic agent in the literature reviewed for this project. The strong antioxidant, antibacterial, and antifungal activities of the plant extract make rosemary an effective food preservative with fewer side effects than artificial additives. The potent antioxidant compounds present in its extract and essential oil explain many of rosemary’s biological activities, including its antidiabetic and anticancer mechanisms.
- World Health Organization. WHO Traditional Medicine Strategy 2014-2023. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241506096
- Rankou H, Culham A, Jury S, Christenhusa MJM. The endemic flora of Morocco. Phytotaxa. 2013;78(1):69. Available from: https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.78.1.1
- Hamidpour R, Hamidpour S, Grant Elias G. Rosmarinus officinalis (rosemary): a novel therapeutic agent for antioxidant, antimicrobial, anticancer, antidiabetic, antidepressant, neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, and anti-obesity treatment. Bio. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2017;1:2574-1241. Available from: https://biomedres.us/pdfs/BJSTR.MS.ID.000371.pdf
- González-Trujano ME, Peña EI, Martínez AL, Moreno J, Guevara-Fefer P, Déciga-Campos M, et al. Evaluation of the antinociceptive effect of Rosmarinus officinalis L. using three different experimental models in rodents. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007 May 22;111(3):476-82. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2006.12.011
- González-Vallinas M, Reglero G, Molina AR. Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) extract as a potential complementary agent in anticancer therapy. Nutrition and Cancer. 2015;67(8):1223-31. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/01635581.2015.1082110
- Anonymous. The Autonomous Establishment for Export Control and Coordination. 2014.
- Damerdji A. Malacological fauna on different medicinal plants in the Tlemcen region (north-western Algeria). Af. Sci. 2012;8:79-87.
- Bock B. Tela Botanica Nomenclatural Database of the Flora of France. 2008;1.
- Sanon E. Trees and shrubs in Algeria. O.P.U. Ben Aknoun. Algeria. 1992;N°686:121.
- Debazac E. Conifer Handbook. E.N.G.R.E.F.-Nancy. 1991;2nd ed:172.
- Hoefler C. Contribution to the pharmacological study of extracts of Rosmarinus officinalis and in particular young shoots: choleretic, antihepatotoxic, anti-inflammatory, and diuretic activities. Doctoral thesis. Option: Human medicine and pathology. Paul Verlaine University – Metz, France. 1994;148. Available from: https://hal.science/tel-01776859/
- Leplat M. Le romarin, Rosmarinus officinalis L., a medicinal Lamiaceae of the Provençal garrigue. Doctoral thesis. Option: Pharmacy. University of Aix. Faculty of Pharmacy. Marseille, France. 2017;229. Available from: https://dumas.ccsd.cnrs.fr/dumas-01550355v1/file/LEPLAT%20Marion.%20Th%C3%A8se%20d%27exercice%202017.pdf
- Teuscher A, Lobstein A. Aromatic plants: spices, seasonings, condiments, and essential oils. Ed. Lavoisier, Paris, 2005;522.
- Borges RS, Ortiz BLS, Pereira ACM, Keita H, Carvalho JCT. Rosmarinus officinalis essential oil: A review of its phytochemistry, anti-inflammatory activity, and mechanisms of action involved. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019;229:29-45. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2018.09.038
- Naggar M, Iharchine K. For a sustainable management and planning approach for rosemary territories in the Oriental region (Morocco). Forêt méditerranéenne. 2016;36(1):63-70. Available from: https://hal.science/hal-03556486/document
- Gilly G. Aromatic plants and essential oils in Grasse. Harmattan Edition. 2005;418.
- United States Agency for International Development (USAID). Aromatic & Medicinal Plant Sector Project. 2006; Chemonics International Inc. Contract no 608-M-00-05-00043-01. Available from: https://pdf.usaid.gov/pdf_docs/Pnadp288.pdf
- Barceloux DG. Pepper, and Capsaicin (Capsicum and Piper species). Dis Mon. 2009;55:380-90. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.disamonth.2009.03.008
- Staub H, Bayer L. Advanced treatment of phyto-aromatherapy: with presentation of 750 known essential oils. Paris: Grancher, 2013; 685.
- Harrane A. Ecology and systematics of the genus Rosmarinus L. in the south Algerian region. Doctoral thesis. Option: Ecology and Environment. University of Science and Technology Houari Boumediene. Djelfa, Algeria. 2012; 119.
- Ghedira K. Flavonoids: structure, biological properties, prophylactic role, and therapeutic uses. Phytothér. 2005;3:162-169. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10298-005-0096-8
- Karadag AE, Çaşkurlu A, Demirci F, Okur ME, Orake D, Sipahi H, et al. In vitro antibacterial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic evaluation of extracts from Rosmarinus officinalis L. flowers. J. Sud Afr. Bot. 2019;125:214-220. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2019.07.039
- Bulut G, Tuzlacı E. An ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants in Bayramiç (Çanakkale, Turkey). Marmara Pharm J. 2015;19:268-282. Available from: https://www.jrespharm.com/uploads/pdf/pdf_MPJ_393.pdf
- Afolayan AJ, Mbaebie BO. Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used as antiobesity remedies in Nkonkobe Municipality of South Africa. Pharmacog J. 2010;2:368-373. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0975-3575(10)80017-3
- Van Wyk BE, De Wet H, Van Heerden FR. An ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants in the southeastern Karoo, South Africa. S Afr J Bot. 2008;74:696-704. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2008.05.001
- Fedjer Z, Mazari AA, Blama A. Ethnobotanical study with the riverside population of Souk Ahras: Case of rosemary in Taoura and prickly pear in Sidi-Fredj. Agronomical Research. 2022;20(1):43-60. Available from: https://asjp.cerist.dz/en/article/191425
- Arnold N, Valentini G, Bellomaria B, Laouer H. Comparative study of essential oils from Rosmarinus eriocalyx Jordan & Fourr. of Algeria and R. officinalis L. from other countries. Research on Essential Oils. 1997;9:167-175. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/10412905.1997.9699454
- Akshay K, Swathi K, Bakshi V, Boggula N. Rosmarinus officinalis L.: an updated review of its phytochemistry and biological activity. J Drug Deliv Ther. 2019;9:323-330. Available from: https://jddtonline.info/index.php/jddt/article/view/2218
- Othman NM, Elhawary YM, Elbeltagy MG, Badr AE. The effect of Rosmarinus officinalis as a potential root canal medication on the viability of dental pulp stem cells. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2023;24:623–631. Available from: https://doi.org/10.5005/jp-journals-10024-3570
- Meccatti VM, Figueiredo-Godoi LMA, Pereira TC, de Lima PMN, Abu Hasna A, Senna LB, Marcucci MC, Junqueira JC, de Oliveira LD. The biocompatibility and antifungal effect of Rosmarinus officinalis against Candida albicans in the Galleria mellonella model. Sci Rep. 2022;12:15611. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-19425-9
- De Macedo LM, dos Santos ÉM, Ataide JA, de Silva GTSE, de Guarnieri JPO, Lancellotti M, Jozala AF, Rosa PCP, Mazzola PG. Development and evaluation of an antimicrobial formulation containing Rosmarinus officinalis. Molecules. 2022;27:5049. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27165049
- Günther M, Karygianni L, Argyropoulou A, Anderson AC, Hellwig E, Skaltsounis AL, Wittmer A, Vach K, Al-Ahmad A. The antimicrobial effect of Rosmarinus officinalis extracts on oral initial adhesion ex vivo. Clin Oral Investig. 2022;26:4369–4380. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-022-04400-5
- Leontopoulos D, Siafaka A, Markaki P. Black olives as the substrate for Aspergillus parasiticus growth and aflatoxin B1 production. Food Microbiol. 2003;20(1):119-126. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0740-0020(02)00080-1
- Rasooli I, Fakoor MH, Yadegarinia D. Antimycotoxigenic characteristics of Rosmarinus officinalis and Trachyspermum copticum L. essential oils. Int J Food Microbiol. 2008;122:135-139. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.11.048
- Ghaedi M, Yousefinejad M, Safarpoor M, Khafri HZ, Purkait MK. Rosmarinus officinalis leaf extract mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and investigation of its antimicrobial properties. J Ind Eng Chem. 2015;31:167–172. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2015.06.020
- Ture H, Eroglu E, Ozen B, Soyer F. Physical properties of biopolymers containing natamycin and rosemary extract. Int J Food Sci Technol. 2009;44(2):402–408. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2008.01785.x
- Jeevalatha A, Kalaimathi RV, Basha AN, Kandeepan C, Ramya S, Loganathan T, et al. Profile of bioactive compounds in Rosmarinus officinalis. J Drug Deliv Ther. 2022;12(1):114–122. Available from: https://jddtonline.info/index.php/jddt/article/view/5189
- Aruoma OI, Spencer JP, Rossi R, Aeschbach R, Khan A, Mahmood N, et al. An evaluation of the antioxidant and antiviral action of extracts of rosemary and Provencal herbs. Food Chem Toxicol. 1996;34:449-456. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-6915(96)00004-x
- Gillij YM, Gleiser RM, Zygadlo JA. Mosquito repellent activity of essential oils of aromatic plants growing in Argentina. Bioresour Technol. 2008;99(7):2507-2515. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.04.066
- Prajapati V, Tripathi A, Aggarwal K, Khanuja S. Insecticidal, repellent, and oviposition-deterrent activity of selected essential oils. Bioresour Technol. 2005;96(16):1749–1757. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.01.007
- Nassu RT, Gonçalves LAG, Pereira da Silva MAA, Beserra FJ. Oxidative stability of fermented goat meat sausage with different levels of natural antioxidant. Meat Sci. 2003;63(1):43-49. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0309-1740(02)00051-7
- Wang YZ, Fu SG, Wang SY, Yang DJ, Wu YHS, Chen YC. Effects of a natural antioxidant, polyphenol-rich rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) extract, on lipid stability of plant-derived omega-3 fatty-acid rich oil. LWT. 2018;89:210-216. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.10.055
- Balentine CW, Crandall PG, O’Bryan CA, Duong DQ, Pohlman FW. The pre- and post-grinding application of rosemary and its effects on lipid oxidation and color during storage of ground beef. Meat Sci. 2006;73(3):413–421. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2005.12.003
- Fernández-López J, Zhi N, Aleson-Carbonell L, Pérez-Alvarez JA, Kuri V. Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of natural extracts: application in beef meatballs. Meat Sci. 2005;69(3):371-380. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2004.08.004
- Atik Bekkara F, Bousmaha L, Taleb Bendiab SA, Boti JB, Casanova J. Chemical composition of essential oil from Rosmarinus officinalis L. growing spontaneously and cultivated in the Tlemcen region. Biol Santé. 2007;7:6-11.
- Cheung S, Tai J. Anti-proliferative and antioxidant properties of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis). Oncol Rep. 2007;17(6):1525-1531. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17487414/
- Bakirel T, Bakirel U, Ustuner KO, Gunes US, Yardibi H. In vivo assessment of antidiabetic and antioxidant activities of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) in alloxan-diabetic rabbits. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008;116:64-73. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2007.10.039
- Adsersen A, Gauguin B, Gudiksen L, Jäger AK. Screening of plants used in Danish folk medicine to treat memory dysfunction for acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006;104:418-422. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2005.09.032
- Ramadan KS, Khalil OA, Danial EN, Alnahdi HS, Ayaz NO. Hypoglycemic and hepatoprotective activity of Rosmarinus officinalis extract in diabetic rats. J Physiol Biochem. 2013;69:779–783. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-013-0253-8
- El-Demerdash FM, Abbady EA, Baghdadi HH. Oxidative stress modulation by Rosmarinus officinalis in creosote-induced hepatotoxicity. Environ Toxicol. 2016;31:85–92. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22024
- Bousbia N. Extraction of essential oils rich in antioxidants from natural products and agro-food co-products. Thesis. University of Avignon and Pays de Vaucluse and École Nationale Supérieure Agronomic, Algiers; 2011:128. Available from: https://theses.hal.science/tel-00915117v1
- Bourgeois I. The great book of aromatic plants. Rustica editions; Paris. 2007;191.
- Chaitanya MVNL, Ramanunny AK, Babu MR, Gulati M, Vishwas S, Singh TG, et al. Journey of rosmarinic acid as biomedicine to nano-biomedicine for treating cancer: current strategies and future perspectives. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14:2401. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4923/14/11/2401#
- Damianova S, Tasheva S, Stoyanova A, Damianov D. Investigation of extracts from rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) for application in cosmetics. J Essent Oil Bear Plants. 2010;13:1–11. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/0972060X.2010.10643784
- Gupta A, Malviya R, Singh TP, Sharma PK. Indian medicinal plants used in hair care cosmetics: a short review. Pharm J. 2010;2:361–364. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0975-3575(10)80110-5
- Takayama KS, Monteiro MC, Saito P, Pinto IC, Nakano CT, Martinez RM, et al. Rosmarinus officinalis extract-loaded emulgel prevents UVB irradiation damage to the skin. An Acad Bras Ciênc. 2022;94:e20201058. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765202220201058

Article Alerts
Subscribe to our articles alerts and stay tuned.
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 Save to Mendeley
Save to Mendeley
