Open Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics
Headache: A burden in female life and its self-care
1Research Scholar, Department of Pharmacy Practice, Pratishta Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Suryapet, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
2Research Scholar, Department of Pharmacy Practice, Avanthi Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
3Professor and Head, Department of Pharmacy Practice, Pratishta Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Suryapet, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
Author and article information
Cite this as
Nagavamsidhar M, Kiran H, Qadrie ZL, Suman A, Athifa B, et al. (2019) Headache: A burden in female life and its self-care. Open J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2019; 4(1): 004-007. Available from: 10.17352/ojpp.000009
Copyright License
© 2019 Nagavamsidhar M, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.Background: Headache is one of the deliberating disease affecting all most all population around the globe. There are classifi ed according to ICH guidelines and well explained with three hypotheses. Management includes both pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatment. In female, period between menarche and menopause is bonded with frequent headache due to hormonal fl uctuations which can be managed with couple of medications and lifestyle modifi cations.
Objectives: To know the frequency and self-care of headache in young adult females and to determine the trigger factors of headache in them.
Methods: In this cross-sectional study, a validated self-administered, questionnaire was used to collect data among female about 17-24 years.
Headache is the most common disorder affecting human beings throughout the globe. It is generally classified into primary and secondary headache. Often which migraine, tension and cluster type are primary and symptomatic of organic disease is secondary [1]. Pathophysiology of headache is explained by three hypothesis namely vascular hypothesis, platelet hypothesis and central nervous system hypothesis [2]. The WHO has rated migraine amongst the top 20 most disabling life time conditions. It affects people of all groups, sexes, races and social classes around the globe. Migraine can occur due to various trigger factors like stress, emotions, environmental factors, genetic factors, diet, sleep disturbances hormonal factors (menstruation, oral contraceptives) [3].
Hormonal changes in women: Migraine is more common in female than men i.e. 3 times due to fluctuations in estrogen. Women with a history of migraines often report headaches immediately before (PMS) or during their periods (Menstrual migraine) and have a major drop in estrogen and increase in tendency to develop migraines during pregnancy or menopause. Hormonal medications, such as oral contraceptives and hormone replacement therapy, also may worsen migraines by fluctuating the hormone levels in female body [4].
Foods: Aged cheeses, salty foods and processed foods may trigger migraines. Skipping meals or fasting also can trigger attacks. (Table 1)
a. Food additives: The sweetener aspartame and the preservative monosodium glutamate (MSG), found in many foods, may trigger migraines.
b. Drinks: Alcohol, especially wine, and highly caffeinated beverages may trigger migraines.
c. Stress: Stress at work or home can cause migraines. Events causing emotional stress can trigger a migraine headache and Factors related to stress include anxiety, worry, shock, depression, excitement, and mental fatigue. Stress is also an important factor in tension-type headache and Chronic and repeated stress will cause daily or almost daily tension-type headache [5-11].
d. Sensory stimuli: Bright lights and sun glare can induce migraines, as can loud sounds. Strong smells including perfume, paint thinner, secondhand smoke and others can trigger migraines in some people.
e. Changes in wake-sleep pattern: Missing sleep or getting too much sleep may trigger migraines in some people, as can jet lag.
f. Physical factors: Intense physical exertion, including sexual activity, may provoke migraines.
g. Changes in the environment: A change of weather or barometric pressure can prompt a migraine.
h. Medications: Oral contraceptives and vasodilators, such as nitroglycerin, can aggravate migraines [6].
Pain management of headache can be carried out using non-pharmacological like lifestyle, self-care, diet and home remedies like drink plenty of water to stay hydrated, lie down in a dark, quiet room, place an ice bag or cold cloth to your head, massage the area where you feel pain. Perform deep breathing or other relaxation exercises and pharmacological using simple analgesics, NSAIDs, derivatives of ergots, triptans etc. on another hand yoga, cognitive behavioral therapy and hormonal replacement therapy can also help in managing headache in women.
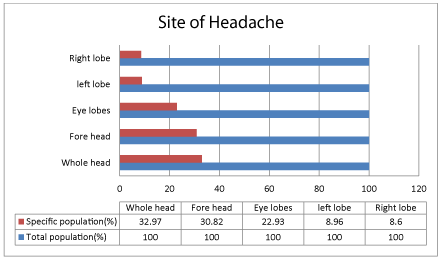
In general, headache can occur on single i.e., left or right side or both and even back or forehead including eye lobes, based on the site of pain the type of headache can be diagnosed i.e. for migraine (one or both side, Aura, eye lobes), tension headache (forehead) and various causes are responsible for left or right side headache which were given in table 2.
Factors triggering Headache in Frontal lobe: (8-11)
The following factors are responsible for triggering Headache in frontal lobe.
a. Sinus infection
b. Jaw or neck pain
c. Allergies
d. Eye strain from computer use
e. Insomnia or other sleep disorders
f. Certain foods, such as meats with nitrates
g. Alcohol, especially red wine
h. Dehydration
i. Depression and anxiety
j. Weather changes
k. Poor posture
l. Tension
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted in a pharmacy colleges were female of age between 17-23 years were taken in to study. A closed end questionnaire was prepared and collected within a period of three months. This conduct of study was limited to class room with permission of respective class in charge. These studies was conducted to known about frequency of headache in daily life and menstrual cycle, triggers and its management in female students and These respective results were obtained using Microsoft word and excel.
Results
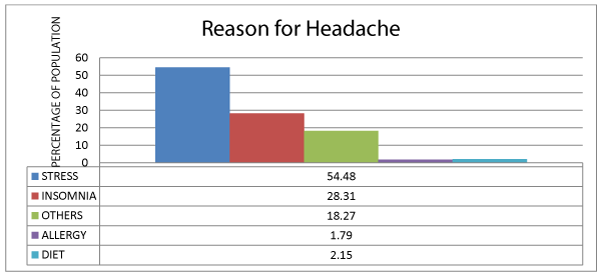
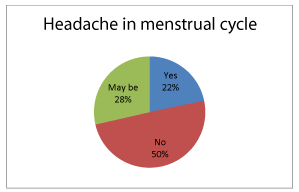
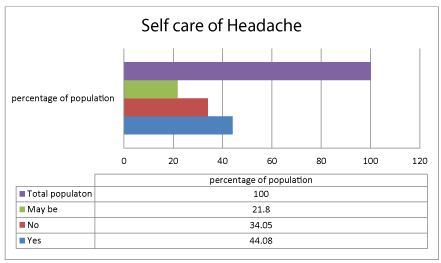
A total number of 279 teenage girls were participated in study. On collection of questionnaire it was found that 89.20 % of girls shows frequent headache in a week that may be of once, twice or even thrice and 11.11 % shows no frequent headaches. This results in this study found that most of the young adult females were affected with various trigger like stress (54.8%), insomnia (28%) and other factor like eye sight, light sensitivity and sinus etc., shows less effect on headache this was shown briefly in the following figure 1. On other hand, it was found that one in every five young adult female i.e., 20 % was noticed to have headache in menstruation cycles. It was also noticed that maximum population in our study had their sleep up to 8 hours and minimum 5-6 hours. Finally, gathered information about self-management of headache in this study group whose response is about having self-care (44%), may be (21.8%) and no self-care (34%). Self-care includes medication like OTC analgesics and life style changes.
Discussion
Headache in human life has become burden especially migraine which is more common in female than in male. Headache in female life is common due to hormonal changes i.e., fluctuations in estrogen levels in menstrual cycle, pregnancy and menopause. Even some women face this sign in sexual activities, heavy work load (stress) or may be due emotional stress. On other hand serotonin interacts with female sex hormones that plays role in provoking headache. In our study, it is found that around 22 % with menstrual headache that may be accompanied with other symptoms like acne, arthralgia and increased appetite and craving for caffeine related products and chocolates. On other hand, 28 % may have a chance of headache in menses and 50% have no complaints of headache in menstruation (Figure 2). In the present study, results shown that most of the young adult females were affected with various trigger like stress (54.48%), insomnia (28.31%) and other factor like diet, allergy eye sight, light sensitivity and sinus etc., shows less effect on headache. This results supports that stress may be mechanical or emotional shows as trigger to migraine [12]. Insomnia is second reason for headache in female and teenagers due to high intake caffeinated products in nights or close to bed time or disturbances in sleep-wake rhythm. The site of headache that correlates with reasons for headache sees above table 2. Self-care of headache in females was found that 44 % of the study population undergo self-management (Figure 3,4) and self-care include self-medication, relieving stress, meditation, sleep etc. Using analgesics, NSAID’s for reducing pain related to headache and even menstrual cramps. Around 47.295% of population use analgesics for headache management, remaining 52.705% use other anti-migraine drugs like antidepressants, ergotamines, estrogen pills and triptans for managing headache. Triptans are most effective treatment in managing migraine, tension type headache and PMS headache. Estrogen pills are commonly used in females at menopause due to fluctuations in hormones. Non-pharmacological management include relaxation techniques, sleep, yoga, avoiding triggering foods like caffeinated drinks, glutamate foods etc. and Psychotherapy, biofeedback therapy etc [4].
Conclusion
Headache is most common sign for both men and women but in female it is more compared to men due to hormones and their fluctuations interfere with serotonin leads to vascular changes. There are various triggers for headache and some of them are reversible with changes in diet, lifestyle and relaxation. Stress and sleeplessness can be managed by relaxation and biofeedback, yoga and psychotherapy with the help of healthcare team.
- Beckett BE, Herndon KC (2005) Headache Disorders, Pharmacotherapeutics- A Pathophysiologic Approach, 6th Edition, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. United States 1119-1135.
- Muthyala N, Qadrie ZL, Suman A (2018) Migraine & Migraine Management: A Review; PharmaTutor 6: 8-17. Link: http://bit.ly/2Y5ansj
- Link: http://bit.ly/30AGzBG
- A Patient Guide to Menstrual Headache Link: http://bit.ly/2LWQRrN
- Link: http://bit.ly/2SgIcl5
- Link: http://bit.ly/32r17OR
- Link: https://mayocl.in/2LUyC61
- Link: http://bit.ly/2LWSZ2C
- Link: http://bit.ly/32tlxGT
- Lipton RB, Rapoport AM (1996) Migraine with and without aura, in Office Practice of Neurology, MA Samuels and S Feske, eds., Churchill Livingstone, New York 1105–1111.
- Link: https://cle.clinic/2YUlku7
- Link: http://bit.ly/2SsDPnb
Article Alerts
Subscribe to our articles alerts and stay tuned.
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 Save to Mendeley
Save to Mendeley
